
Hearing Aids 2025: Everything You Need to Know
If you’re considering hearing aids, you’re likely to have a lot of questions. What do hearing aids look like? How big are they? Is there an invisible option for me? How much do they cost, and where can I buy them?
Once you acknowledge your hearing difficulties, the solution is within reach: hearing aids can make a real difference. But with so many options available, how do you choose the right one? What can modern hearing aids do? What factors should you consider when making a decision? Our comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know.
Table of contents
Digital hearing aids: HighTech for your ears
Today’s hearing aids are fully digital. Instead of visible transistors and capacitors, they contain powerful processors that don’t just amplify sound but refine it. This allows the audio experience to be tailored to your specific needs. The latest models even utilize artificial intelligence to create a more natural sound environment, significantly enhancing your hearing experience.
a) Essential features: What does a hearing aid user need?
The most critical factor is your hearing test results and individual hearing profile. How much amplification do you need at different frequencies? Which tones require more support, and which don’t? A digital signal processor in the hearing aid calculates precise amplification levels for each frequency, ensuring that extra volume is only applied where necessary. It also respects your personal volume limits to prevent discomfort from sounds that are too loud.
b) Nice-to-have features: What does a hearing aid user want?
Advanced processors can actively manage background noise. If you’re sensitive to certain sounds, your hearing aid can be adjusted to reduce them according to your preference. Different types of noise – such as wind, driving noise or vacuum cleaners – can be processed separately from speech or music. This level of customization is only possible with fully digital signal processing.
Expert Tip: Before your consultation with a hearing specialist, take note of the listening situations where you’d like improvement. This will help ensure you get the best recommendations.
Style, size and descretion: What do hearing aids look like?
Hearing aids are categorized by how they are worn. Some have a small housing that sits behind the ear, with sound transmitted into the ear canal via a tube or wire. Others are entirely self-contained within a small shell that fits directly inside the ear canal. Each design has its own advantages and is suited to different hearing needs.
By understanding these factors, you can make an informed decision and find the perfect hearing aid for your lifestyle.
Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids
There are three main types of behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids:

Standard Tube BTE: The Classic Model
This is the traditional type of hearing aid, available for decades but less popular today due to its larger size. The hearing aid’s casing, which contains all the electronic components, sits behind the ear. Amplified sound is directed into the hearing angle and then transmitted via a plastic tube into the ear canal. The tube is secured inside a custom earmold (otoplastic) that helps with fit and acoustic sealing.
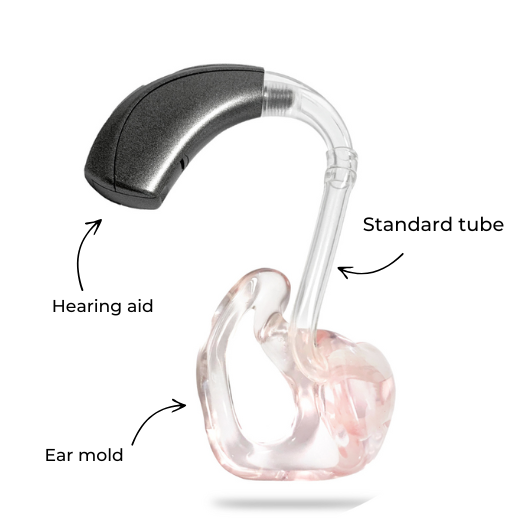
How It Works:
The entire hearing technology is housed in the casing behind the ear. A plastic tube connects it to a custom earmold.
While the plastic tube is flexible, it needs to be replaced approximately every three months. Acoustically, this tube system has some drawbacks—sound waves experience friction, which leads to high-frequency sound loss. Due to its larger size, this type of hearing aid is often considered less discreet.
Who can use it
Standard tube BTE hearing aids are suitable for all levels of hearing loss, from mild to profound. They are available in basic, mid-range, and premium models, offering various levels of technology and features.
| Advantages of Standard tube BTE | Disadvantages of Standard tube BTE |
|---|---|
| Easy to handle, even for those with limited dexterity | Large and visible |
| Can use long-lasting batteries or rechargeable options | Significant skin contact |
| Available with a wide range of technologies | Poorer high-frequency transmission |
| Supports all levels of hearing loss | Sound loss due to tube friction |
| Tube replacement requires professional service |
Slim tube BTE: A more discreet option
The design is similar to the standard tube BTE, but the tube is significantly thinner, making it more discreet and visually less noticeable. It also feels lighter and more comfortable on the ear.
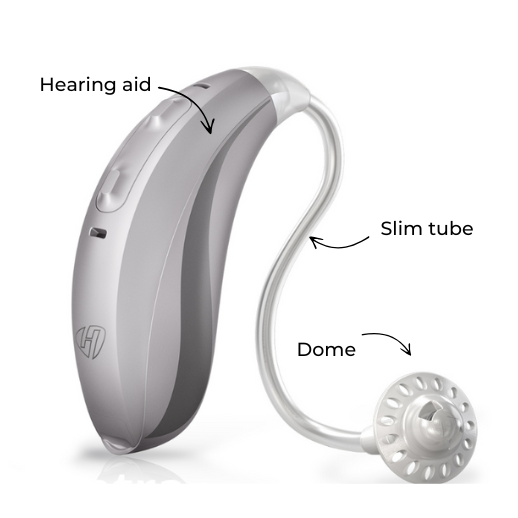

How it works:
The hearing technology is housed behind the ear, and a thin plastic tube transmits the sound into the ear canal.
However, because the tube is even narrower than in the standard BTE, sound friction losses are greater, leading to more high-frequency sound loss. The tubes are rigid rather than flexible and come in different lengths for the right and left ear. They are easy to clean with dental floss but can kink easily and should be replaced every three to six months. Most slim tube BTE models come in various price ranges and technology levels, but they generally do not allow for high amplification levels. Some models allow users to switch between standard and slim tubes using a simple adapter, which the hearing specialist must account for when programming the device.
| Advantages of Slim tube BTE | Disadvantages of Slim tube BTE |
|---|---|
| More discreet than standard BTE | Still somewhat visible |
| Comfortable to wear | High-frequency sound loss |
| Can use long-lasting batteries or rechargeable options | Sound loss due to tube friction |
| Supports various hearing technologies | Not suitable for severe hearing loss |
| Tubes are fragile and less durable |
RIC (Receiver-in-canal) BTE: The modern favorite
RIC (Receiver-in-Canal) hearing aids have rapidly become the most popular type of BTE. Unlike tube-based models, RIC devices separate the speaker from the main hearing aid casing. The speaker is placed inside the ear canal and is connected to the main device by a thin wire.
This separation allows for much smaller casing designs compared to tube-based models.
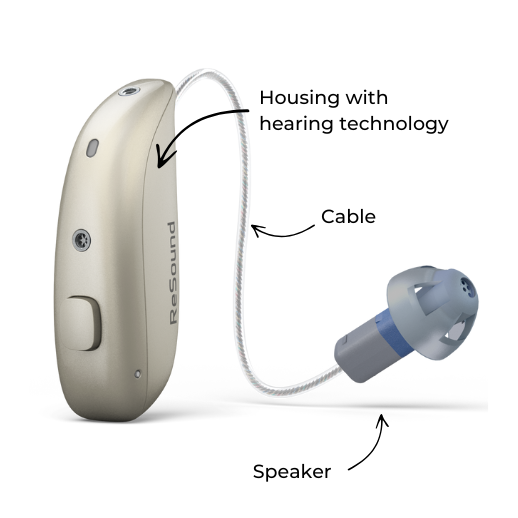

How it works:
Most of the electronics are housed in the casing behind the ear, while the speaker sits inside the ear canal, connected by a thin wire.
Acoustic Advantages:
Because the speaker is positioned closer to the eardrum, there is minimal sound loss, and the amplification reaches the ear with near-perfect clarity. This results in superior sound quality compared to tube-based models.
Additionally, RIC models offer flexibility: the speaker unit comes in different power levels, so if hearing loss worsens, the specialist can swap out the speaker for a more powerful one and reprogram the device—no need for a completely new hearing aid.
Due to this versatility, comfort, and performance, RIC hearing aids are now a leading choice, even for individuals with severe hearing loss.
| Advantages of RIC BTE | Disadvantages of RIC BTE |
|---|---|
| Small and discreet | May be more challenging to handle |
| Excellent high-frequency sound transmission | Can be more expensive |
| Outstanding sound clarity | |
| Works with batteries or rechargeable options | |
| Supports various hearing technologies | |
| Compatible with all levels of hearing loss | |
| Very comfortable to wear |
BTE hearing aids typically come with larger batteries, offering longer battery life—sometimes lasting several days. Rechargeable models are also widely available. Most BTE devices work for both mild and severe hearing loss, and they often have manual control buttons for adjustments.
While BTE hearing aids are never entirely invisible, they range from very discreet to more noticeable models, depending on the size and design.
In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids are custom-made to ensure a perfect fit, preventing them from falling out of the ear. A hearing specialist first takes an impression or 3D scan of the outer ear and ear canal. Skilled professionals then use computer-aided design to create a custom shell, which is produced with a 3D laser printer and carefully assembled with acoustic components.
Since all components are housed within a compact shell, the device sits inside the ear canal to varying depths depending on the model.
The four types of ITE hearing aids




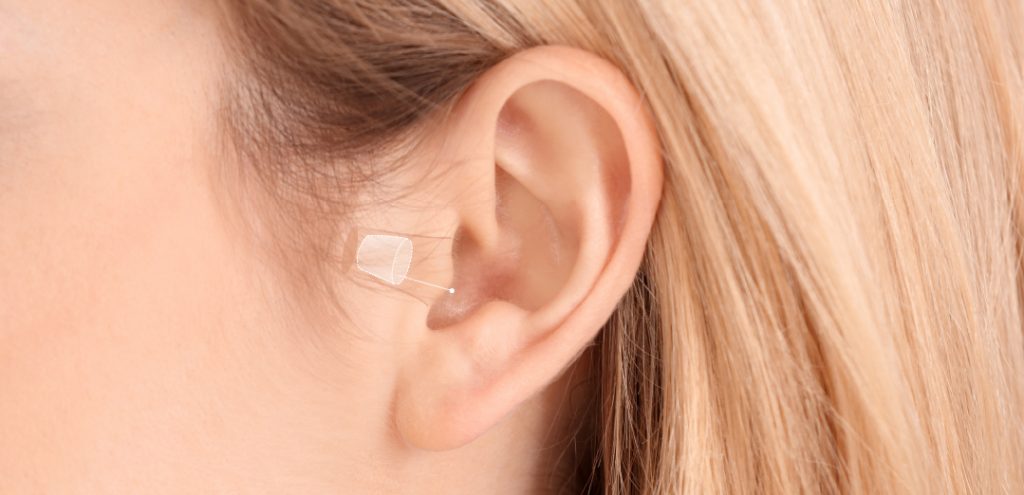
IIC (Invisible-in-canal) hearing aids
IIC hearing aids are the smallest on the market. If the ear canal is deep enough, they become completely invisible, sitting just before the eardrum. Despite their tiny size, they provide enough amplification for most hearing losses.

| Advantages of IIC | Disadvantages of IIC |
|---|---|
| Completely invisible | Only suitable for mild to moderate hearing loss |
| Almost unnoticeable when worn | May be difficult to handle |
| Well-protected from external influences | Very small battery with a short lifespan |
| Excellent sound quality | Dependent on ear canal size and shape |
| Outstanding high-frequency amplification | Limited technical features |
| Natural spatial hearing |
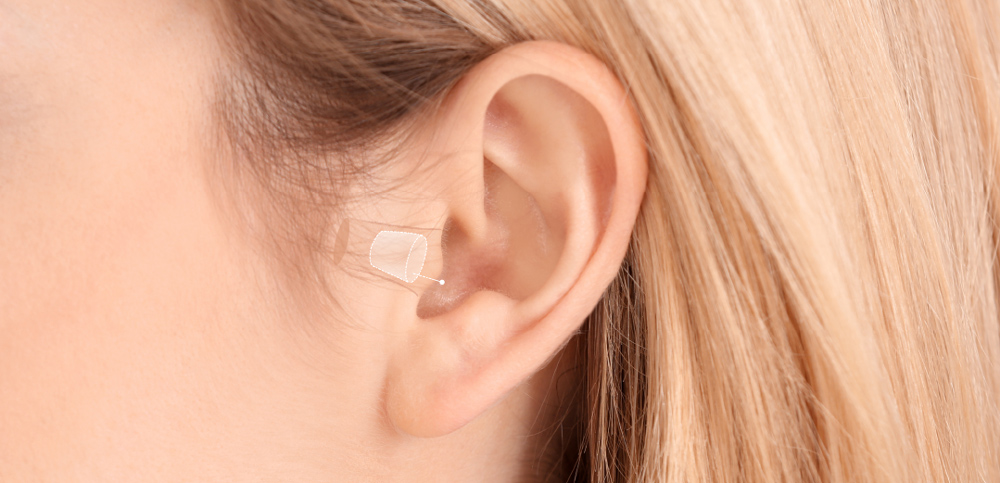
CIC (Completely-in-canal) hearing aids
CIC hearing aids are also very small, sitting in the front part of the ear canal. Depending on available space, they may also be nearly invisible. They offer slightly more room than IIC models, allowing for wireless connectivity such as remote control compatibility. Some CIC models even provide stronger amplification for more severe hearing losses.

| Advantages of CIC | Disadvantages of CIC |
|---|---|
| Very discreet and nearly invisible | May be difficult to handle |
| Excellent sound quality | Very small battery with a short lifespan |
| Outstanding high-frequency amplification | |
| Great spatial hearing | |
| Available for stronger hearing loss |
ITC (In-the-canal) hearing aids
ITC hearing aids are slightly larger, with the front plate visible in the ear bowl. This extra space allows for more advanced technology, such as wireless connectivity to external accessories and direct smartphone pairing. Some models even feature manual controls for volume adjustment. Additionally, ITC hearing aids can accommodate a larger battery, improving battery life.
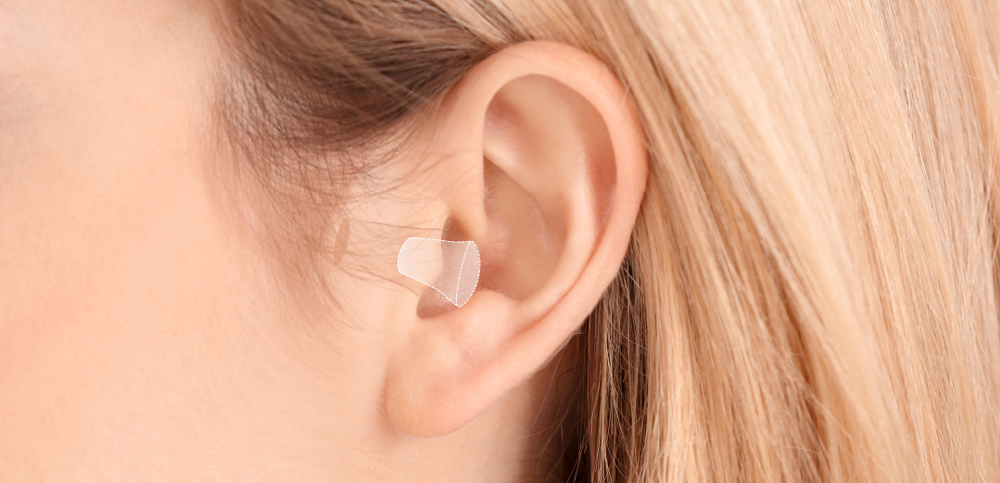
| Advantages of ITC | Disadvantages of ITC |
|---|---|
| Excellent sound quality | Somewhat visible |
| Outstanding high-frequency amplification | More skin contact, making it more noticeable |
| Longer battery life; rechargeable option available | |
| Easier handling for those with motor impairments | |
| Supports all modern hearing technologies | |
| Works for all levels of hearing loss | |
| Allows manual controls if needed | |
| Great spatial hearing |
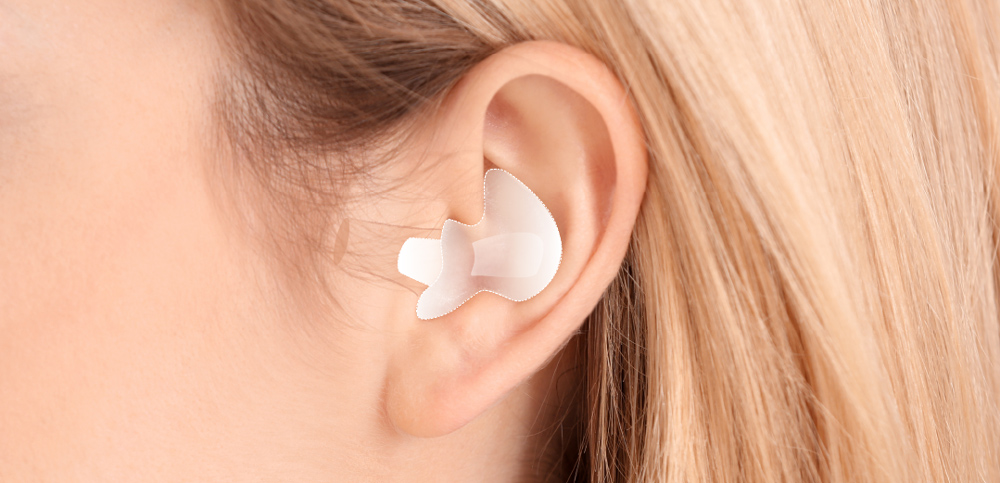
ITE (In-the-ear) hearing aids
ITE hearing aids fill the entire outer ear bowl but do not protrude outward or extend too deeply into the canal. Their larger size allows for more advanced technology, such as Bluetooth and powerful amplification for severe hearing loss. Some ITE models now come with rechargeable batteries for added convenience.

| Advantages of ITE | Disadvantages of ITE |
|---|---|
| Excellent sound quality | More visible than other in-ear models |
| Outstanding high-frequency amplification | More skin contact, making it more noticeable |
| Long-lasting battery or rechargeable option | |
| Easier handling for those with motor impairments | |
| Allows for manual control buttons if needed | |
| Supports all modern hearing technologies | |
| Works for all levels of hearing loss | |
| Provides great spatial hearing |
Instant Fit Hearing Aids
A new category of in-the-ear hearing aids is known as Instant Fit devices. These have a standard shape and do not require custom fitting.
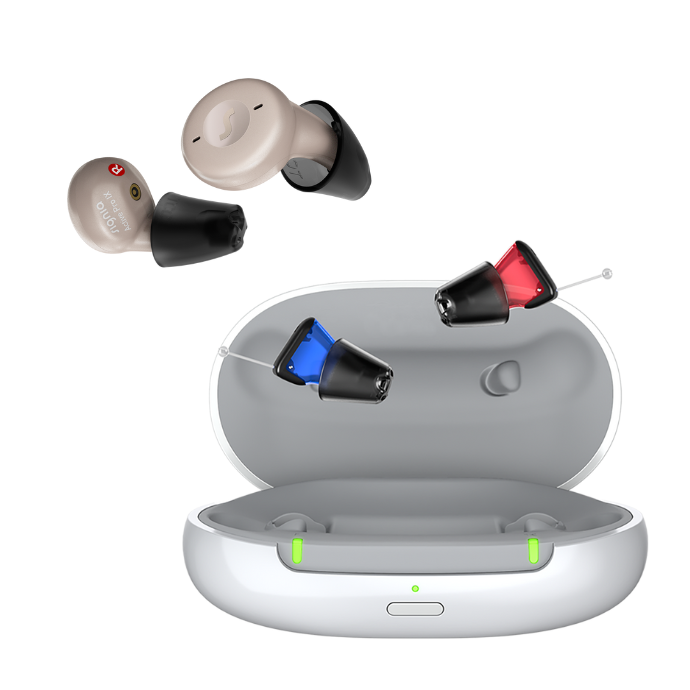

Advantages:
- They can be taken home immediately after programming—no need for custom molds.
- Many models feature a stylish, modern earbud-like design.
Disadvantages:
- The lack of custom fitting may result in a less-than-perfect fit. After all, who has a „standard“ ear canal?
- You might need to adjust them frequently, and there’s a risk of losing them.
- Sound leakage can occur, potentially reducing overall sound performance.
The benefits of In-the-ear hearing aids
All in-the-ear models provide excellent spatial hearing, thanks to their placement inside the ear canal. This allows natural use of head and ear anatomy to determine sound direction, just like natural hearing.
Additionally, in-the-ear devices are compatible with glasses, helmets, and hats, avoiding the interference common with behind-the-ear (BTE) models.
Dispelling myths about In-the-ear hearing aids
Some misconceptions about ITE hearing aids persist, including:
❌ „They block the ear completely.“ – Not true. Ventilation holes are custom-designed for comfort.
❌ „They are only for mild hearing loss.“ – Incorrect. Even small CIC models can now accommodate severe hearing loss thanks to advanced miniaturization.
❌ „They break easily.“ – False. Modern manufacturing ensures durability, and with proper maintenance, ITE and BTE hearing aids have similar lifespans.
Conclusion
ITE hearing aids offer a discreet and comfortable solution with excellent sound quality and technological flexibility. Whether you need a nearly invisible option (IIC/CIC) or a powerful, easy-to-handle model (ITC/ITE), there is an in-the-ear device that suits your needs.
Earmolds, domes & more
Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids need to be securely attached to the ear to ensure a comfortable and stable fit. There are both custom-made solutions and standard attachments available.
Custom earmolds
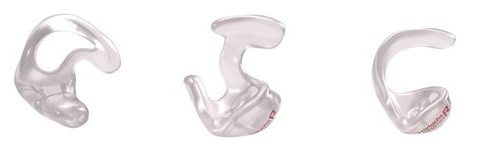
Custom earmolds offer excellent stability and easy handling. They are recommended for:
Very high amplification needs
Users with limited finger dexterity
Optimal acoustic sealing

Miniature earmolds provide minimal skin contact while ensuring a secure fit and clear sound transmission. If placed deeply in the ear canal, a small removal cord can help with easy extraction.
Materials available:
- Hard plastic
- ThermoTec
- Silicone
- Titanium
- Ceramic

Manufacturing process
- The ear and ear canal are impressioned or 3D-scanned.
- Specialists design the earmold on a computer, focusing on both cosmetic and acoustic properties.
- The earmold is produced with a high-performance 3D printer.
- The final step involves smoothing edges and applying a protective skin coating.
Earmolds come in different sizes and shapes, from nearly invisible models to larger, easy-to-handle designs for those with motor impairments.
Expert Tip:
For miniature earmolds, ThermoTec is a great option. It starts out firm for easy insertion, but softens with body heat, enhancing comfort. This material is also breathable, allowing moisture to escape, which supports a healthy ear environment.
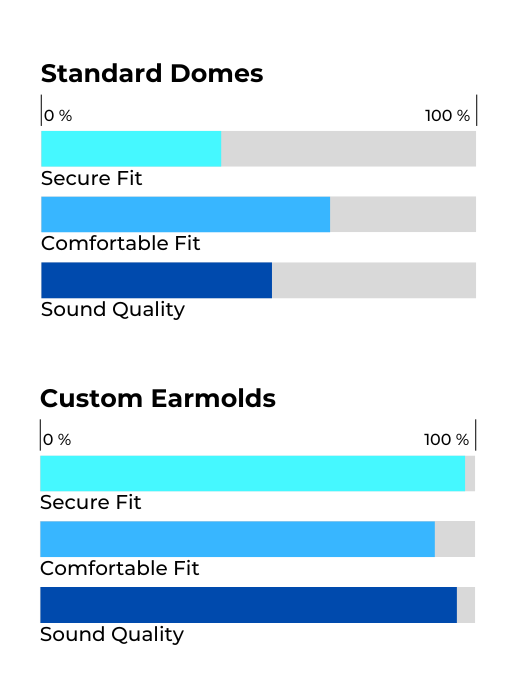
Standard solutions: Domes
Standard domes (also called ear tips) are made from soft, thin material and attach directly to the tube or receiver. They are primarily meant for trial use and are not as durable as custom earmolds.
Important to know:
- Domes wear out quickly and should be replaced every 3 months.
- They do not provide the same secure fit as custom earmolds.
- More external noise enters the ear, reducing the effectiveness of the hearing aid.
- There is a higher risk of sound leakage, which can lead to feedback whistling.

🔹 Hearing professionals strongly recommend custom earmolds over domes.
🔹 Only custom earmolds ensure optimal sound transmission to the eardrum and reduce unwanted background noise.
Conclusion
✔ Secure and comfortable fit
✔ Better sound quality
✔ Prevents feedback whistling
✔ More durable than domes
While domes provide a quick solution, only custom earmolds offer the best combination of comfort, stability, and acoustic performance.
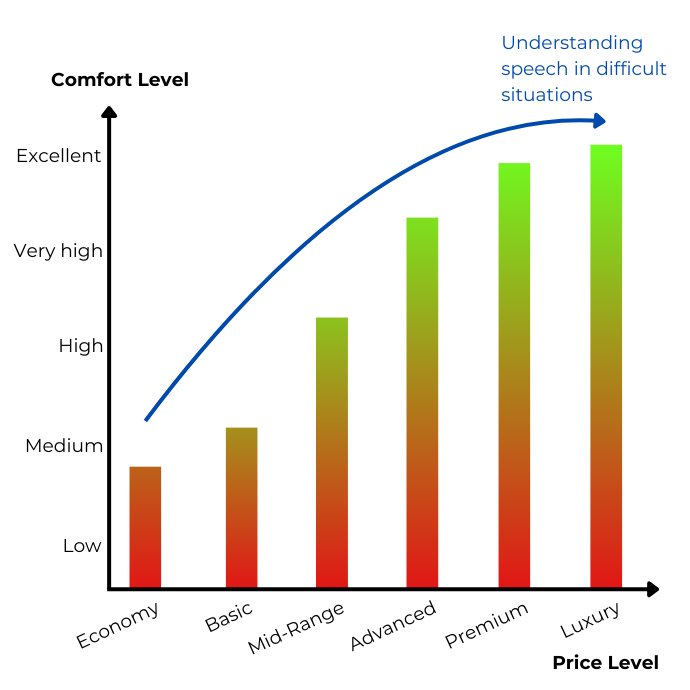
Prices for hearing aids and technical features
Most hearing specialists offer hearing aids in different price ranges. This allows you to decide in advance, after a good consultation, what your hearing comfort expectations are and how much you’re willing to invest.
Of course, even the most affordable hearing aids help with understanding speech. However, the way noise is processed and how complex listening environments are handled determine the overall comfort of hearing and, consequently, the price.
Why do hearing aids have this price?
The price of a hearing aid is primarily influenced by three factors:
- Hearing Comfort
This mainly refers to background noise. What types of sounds are recognized? How effectively are they reduced? How does spatial hearing function? How natural does the sound feel?
Generally speaking, the more you invest in your hearing aids, the less effort is needed to focus while listening. Higher-end devices reduce unwanted sounds to the point that they no longer feel disturbing. Additionally, the sound quality and naturalness improve with the price. The investment directly contributes to daily comfort. - Technical Extras
If you want to use accessories or connect your hearing aids wirelessly to your smartphone, this usually comes at an additional cost. - Design and Size
In general, size doesn’t greatly impact the price. However, very small design hearing aids are often not found in the lowest price range. In-ear devices typically have a slightly higher price due to the higher production costs, as these variants are always individually manufactured.
Hearing comfort: Smart technologies for perfect sound experience
- Noise Reduction
Reduces monotonous, consistent sounds like traffic or machinery noise. This creates a more pleasant listening experience and lessens the effort involved in listening. - Impulse Sound Management
Improves sound comfort by reducing sudden loud sounds. This can help with sharp noises like dishes clattering, keyboard clicks, or footsteps. - Wind Noise Reduction
Detects and minimizes wind noise when outdoors. This improves listening comfort and reduces listening effort significantly, making speech understanding easier in windy environments. - Soft Noise Management
Reduces listening effort by eliminating low-level background noise from sources like air conditioning, ventilation, or computers, creating a quieter listening environment. - Directional Microphones
Effectively identify sources of noise and then filter them out. They focus on the dominant speaker, providing noticeable support in concentrating on the desired conversation. - Automatic Situation Adjustment
Constantly analyzes the acoustic environment and adjusts accordingly. This makes manual switching largely unnecessary. - Wideband Frequency Transmission
The more high-pitched sounds are transmitted, the more natural the sound feels. This significantly improves sound comfort, especially when listening to music. - Binaural Signal Processing
Creates real 3D hearing, enhancing spatial awareness and reliable direction identification. - DNN Signal Processing
DNN (Deep Neural Network) refers to a special chip that operates in a connected, complex structure, mimicking the functionality of the human brain. These chips are often pre-trained with millions of realistic sound scenarios, enabling highly reliable separation of speech and noise. - Wireless Connection to Smartphones & Other Devices
Wireless connectivity with smartphones, laptops, TVs, etc., facilitates multimedia use and improves hearing comfort by reducing listening effort.
AI in hearing aids: A growing role
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in the development of modern hearing aids, especially in chip technology. These devices undergo intensive training, where AI algorithms are specialized to respond precisely to different and changing listening environments. This advanced training allows hearing aids to process acoustic signals better and adjust dynamically to new situations. The result is a significant improvement in speech understanding, making it much easier to hear in challenging environments. The integration of AI into hearing aid development thus greatly enhances quality of life.
Hearing aids: Effective against tinnitus
Many tinnitus sufferers experience significant relief when wearing hearing aids. The amplification provided by the device enriches the auditory pathway with sound, keeping the ear engaged and diverting attention away from the tinnitus. In many cases, this is enough to make the ringing disappear into the background.

However, for some people, this effect isn’t always sufficient—especially in quiet settings when they want to relax, and the tinnitus becomes more noticeable. For these situations, special tinnitus relief programs are available in modern hearing aids.
A hearing specialist can determine the frequency range of the tinnitus and create a customized noise program. The volume and tone of this program can be adjusted to personal preferences, producing a sound similar to ocean waves or a gentle breeze. This broadband stimulation helps the brain shift its focus away from the tinnitus, making it much less noticeable.
Power supply for hearing aids
Hearing aids require a substantial amount of energy to function properly—especially at higher volume levels. Today, you can choose between battery-powered and rechargeable hearing aids.
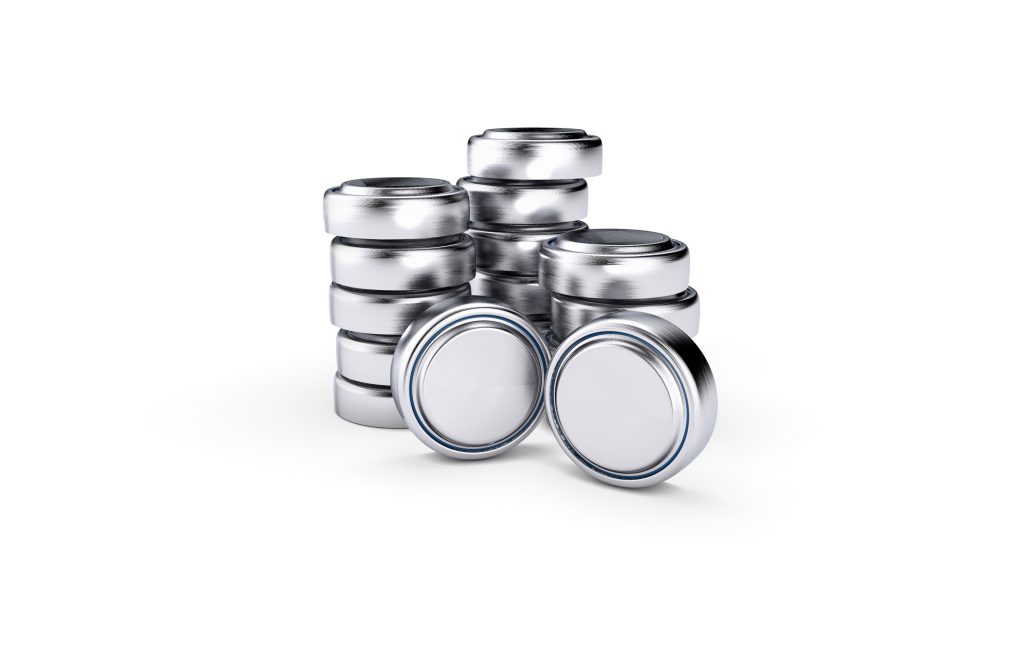
Battery-powered hearing aids
For years, hearing aids have typically been powered by zinc-air batteries. These look like small button cells but function differently.
- Each battery contains zinc powder inside a tiny metal container.
- The top of the battery has air holes that are initially covered by a sticker.
- Once the sticker is removed, oxygen enters and reacts with the zinc to generate electricity.
Zinc-air hearing aid batteries have high energy capacity to meet the power demands of modern hearing aids.
🔋 Battery lifespan (depending on size): 3 to 14 days
🔔 Low battery warning: A signal tone alerts you when a replacement is needed.
Battery Sizes & Color Coding
Hearing aid batteries are standardized and use both color and number codes:
- 🟡 Yellow – ZL 10
- 🟤 Brown – ZL 312
- 🟠 Orange – ZL 13
- 🔵 Blue – ZL 675
Important: Even though they look similar to standard button cells, hearing aid batteries operate differently by utilizing oxygen from the air.

Rechargeable hearing aids: Convenient & efficient
In recent years, rechargeable hearing aids have become a popular alternative. These models typically feature a built-in lithium-ion battery, eliminating the need for disposable batteries.
How It Works:
- The hearing aids are placed in a charging station overnight.
- Within 3 hours, they charge fully for a full day’s use.
- The hearing aids turn on and off automatically when placed in or removed from the charger.
💡 Why rechargeable hearing aids aren’t invisible:
A tiny battery wouldn’t last all day. However, rechargeable models remain compact and stylish, and even in-ear hearing aids now come with built-in rechargeable batteries.
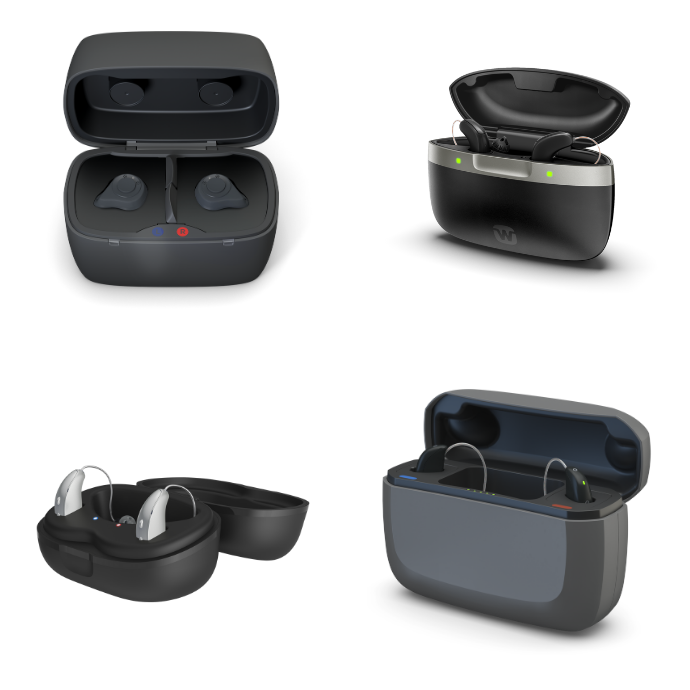

Expert Tip: If you frequently use wireless streaming (for phone calls, TV audio, or music transmitted directly to your hearing aids), a rechargeable model is the best option. Regardless of how much you stream throughout the day, the battery will last the entire day without issues.
Smartphone, TVs & more: Accessories and wireless connections
Most hearing aid users also use a smartphone, but phone conversations can often be challenging. Wireless connectivity between smartphones and hearing aids provides a major advantage.
Many modern hearing aids already have 2.4 GHz wireless technology built in. Apple devices (iPhones and iPads) are fully compatible, even with older models. Android joined the field in 2019, and while not all Android smartphones support direct connectivity yet, the number is steadily growing. Hearing specialists have compatibility lists and can provide recommendations.
Some hearing aids now support Auracast, the new Bluetooth standard. Auracast is an energy-efficient and versatile wireless technology that will soon become widely available in public spaces. In the future, you’ll be able to receive public announcements at train stations and airports, cinema soundtracks, or TV audio in public places via Auracast broadcast channels.
With wireless connectivity, hearing aids become a headset. Phone calls and other audio (music, ringtones, movies, news) stream directly into both ears.
Smartphone apps for hearing aids
Beyond streaming, smartphone apps are now a fun and highly functional way to control hearing aids. They offer a range of adjustments, including:
🎚 Equalizer settings
🎤 Microphone directionality
These features allow for a more personalized hearing experience.

TV streaming for hearing aid users
Wireless TV adapters are a popular accessory that transforms movies and TV shows into immersive experiences by streaming TV audio directly into hearing aids.
- No need for headphones
- Wireless transmission
- Independent volume control
Installation is easy, and adapters come with all necessary cables and connectors.
External Microphones for Better Sound
- Clip-on microphones: Attach to clothing to improve speech clarity in noisy settings.
- Table microphones: Useful for meetings, lectures, and guided tours.
Remote Controls for Hearing Aids
Many hearing aids are compatible with remote controls, allowing:
✅ Volume adjustments
✅ Switching between hearing programs
Users can also use a smartphone app or physical button on the hearing aid instead.

Watching TV with hearing aids
Television is an important source of information and entertainment, but hearing difficulties can make it harder to follow TV dialogue.
This is often because hearing loss affects high-frequency sounds more than lower tones. Simply increasing the volume doesn’t solve the problem—it makes everything louder but not clearer.
Hearing aids offer two solutions:
a) TV-Specific Hearing Programs
Most hearing aids have multiple memory slots for custom hearing programs.
A hearing specialist can optimize one for TV use by:
✅ Enhancing speech frequencies
✅ Boosting softer speech sounds
✅ Compensating for sound loss over distance (e.g., from TV to sofa)
Best practice:
Such programs can be fine-tuned remotely from your own home.
📱 How? Your hearing specialist can adjust settings via an online session while you test it live with your TV.
b) TV Adapters for direct streaming
If a TV program alone isn’t enough, a TV adapter is the next step.
These small devices connect to the TV and convert sound into a wireless signal. The hearing aids receive the sound directly, perfectly synchronized, with zero loss of quality.
Key benefits of TV adapters:
- Hearing aid microphones remain active → You can still talk with family while watching TV.
- No isolation effect → Unlike headphones, you’re still engaged with those around you.
- No distance restrictions → Audio transmission works from anywhere in the room.
- Everyone controls their own volume → No more fights over TV volume settings!
Phone calls with hearing aids
Phones are essential in daily life, but conversations rely almost entirely on hearing. Hearing aids greatly improve call clarity.
Challenges of Phone Calls with Hearing Aids
Phones and hearing aid microphones are not always perfectly aligned, especially with BTE (Behind-the-Ear) hearing aids.
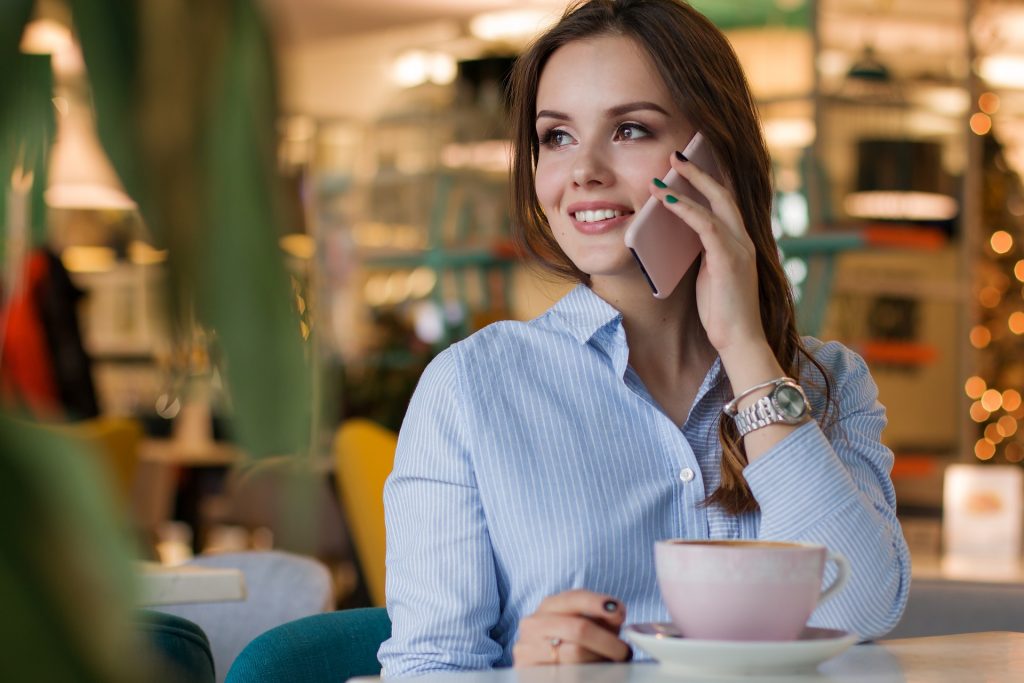

Tips for easier phone calls with hearing aids
1️⃣ Positioning Matters
For BTE users, the microphones sit on top of the ear. Instead of holding the phone against the ear canal, position it slightly higher to ensure the sound is captured properly.
2️⃣ Easier Calls with In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids
ITE hearing aids are inside the ear canal, so they naturally pick up phone audio more effectively.
3️⃣ Special Phone Programs
A hearing specialist can program a dedicated “Phone Mode” into the hearing aids for better call clarity. Some hearing aids automatically detect when a phone is held to the ear and switch to phone mode.
4️⃣ Magnetic Induction (T-Coil / Telecoil)
Some phones generate a magnetic field that can be picked up by hearing aids with a telecoil (T-coil).
🔹 Works with older corded phones or special hearing-impaired telephones.
🔹 Provides direct sound transmission into the hearing aid with zero background noise.
5️⃣ Bluetooth Landline Phones
Many modern landline phones have Bluetooth capability.
✅ Can connect wirelessly to hearing aids via a small streamer.
✅ The streamer includes a microphone, functioning like a hands-free system.
6️⃣ Brand-Specific Phones for Hearing Aids
Some hearing aid manufacturers offer specialized landline phones that connect directly to their hearing aids without extra accessories. However, they only work with specific hearing aid brands.
7️⃣ The Easiest Solution: Smartphone Streaming
Smartphone calls are now easier than ever for hearing aid users.
✅ Hearing aids directly connect to compatible smartphones via wireless streaming.
✅ Calls stream into both ears, improving clarity even in noisy environments.
✅ Works indoors and outdoors with minimal effort.
Expert Tip: If you’re considering buying a new smartphone, ask your hearing specialist for a compatibility list.
This ensures your investment is compatible with modern hearing aids and ready for future wireless updates.
Exercising with hearing aids
Many people wonder if they can wear their hearing aids while exercising. The answer is yes – absolutely! In fact, it’s highly recommended.
Sports often involve social interaction—whether you’re chatting during a jog or following instructions in a yoga class. Hearing aids and sports make a great team! However, there are two important things to keep in mind:
a) Ensuring a secure fit.
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids already fit securely, so there’s no concern.
Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids should ideally be worn with a custom earmold (otoplastic) for added stability.
If you prefer using a dome (ear tip), a concha lock is recommended. This is a thin, almost invisible plastic support that attaches to the receiver wire or thin tube and rests inside the ear for extra hold.
b) Proper care & maintenance
Modern hearing aids come with moisture protection, but sweat can still enter through microphone openings or battery compartments.
To prevent damage, place hearing aids in a drying device every night.
Drying boxes remove moisture and use UV light to disinfect the hearing aids.

Swimming and sauna use are not recommended, as excessive moisture can damage hearing aids. Outdoor sports are fine, even in rain, thanks to water-resistant coatings on hearing aid casings.
Listening to lectures with hearing aids
Attending lectures, seminars, and presentations is much easier with hearing aids. However, certain acoustic challenges exist:
- Speakers are at a distance, making their voices sound softer.
- Large rooms have different acoustics compared to home environments.
- Audience noise can be distracting.

Hearing aids help in two ways:
1) Custom Lecture Mode
A special lecture program can be set up by a hearing specialist.
🎯 Distant voices are amplified.
🔇 Background noise from behind and the sides is reduced.
2) Wireless Microphones
A wireless clip-on microphone can be given to the speaker before the lecture.
✅ The speaker’s voice is transmitted directly to your hearing aids.
✅ Distance and background noise no longer matter—you hear everything clearly.
Cleaning & caring for hearing aids
Keeping your hearing aids in good condition is easy. Regular maintenance ensures long-lasting performance.
1) Cleaning
- Use a special cleaning spray from your hearing specialist.
- Apply the spray to a tissue and wipe the hearing aid, earmold, or dome.
- Pre-packaged disinfectant wipes also work well.
2) Changing Filters
- RIC (receiver-in-canal) and ITE hearing aids have small wax filters over the speaker.
- These prevent dust and earwax buildup.
- Filters are easy to replace and come with a tool for quick changes.
3) Cleaning Tools for Earmolds
- Brushes, wire loops, and cleaning threads help remove dirt from tiny crevices.
- Your hearing specialist can provide a cleaning kit.
4) Using an Ultrasonic Cleaner
- Only needed for tube-based hearing aids (BTE models with earmolds).
- The earmold and tube can be detached and cleaned in an ultrasonic bath.
- Afterward, remove water from the tube using an air puffer or compressed air canister.
5) Drying & Moisture Protection
Rechargeable hearing aids require specialized drying stations that can charge and dry at the same time.
Even with protective filters, moisture can enter hearing aids. Electronic drying devices use warm air to remove moisture. UV light disinfection ensures hygienic cleaning.
Hearing aid manufacturers: Who makes the best hearing aids?
People often ask: Which hearing aid brand is the best?
There’s no single “best” brand – only high-quality, reliable, and innovative devices.
Every manufacturer offers a full range of products, covering all needs. Differences exist in:
✅ Sound quality
✅ Ease of use
✅ Design preferences
However, these differences are subjective, as each person has unique hearing needs.
Top international hearing aid brands
Expert Tip:
📢 Ignore advertising and other people’s opinions.
🎧 Your needs are unique.
👂 Trust your hearing specialist and personal experience.
There is no universal “best” hearing aid—but there is a perfect hearing aid for you!
About the author

